

Therapy for hyperkalemia due to potassium retention includes avoiding drugs that potentially induce hyperkalemia, discontinuing offending agents such as potassium supplements, and ultimately inducing potassium loss. Dash) are often overlooked as a cause of hyperkalemia. Overdoses of digitalis or related digitalis glycosides, such as digoxin, can also lead to hyperkalemia. Other drugs with the potential to cause hyperkalemia include beta-blockers, succinylcholine, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), cyclosporine, heparins, tacrolimus, and excessive dosing of potassium supplements. Medication can also lead to hyperkalemia, most notably those agents that inhibit the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Hyperkalemia can also occur secondarily to metabolic acidosis, insulin deficiency, hyperglycemia, and hyperosmolar states.
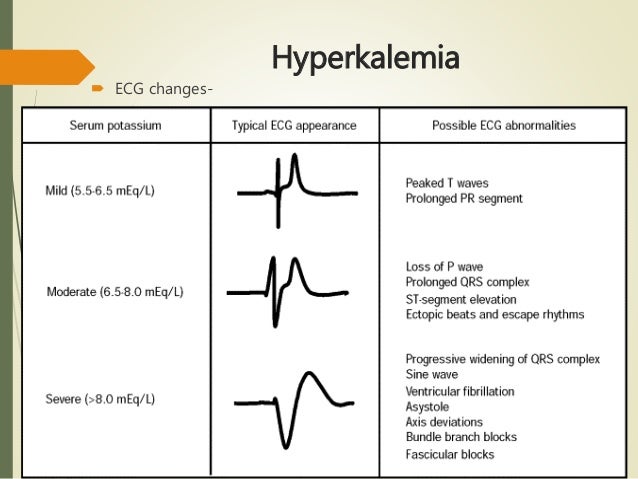
Hyperkalemia is commonly a result of impaired urinary potassium excretion due to acute or chronic kidney disease (CKD), reduced aldosterone secretion, reduced response to aldosterone, reduced distal sodium and water delivery, effective arterial blood volume depletion, or selective impairment in potassium secretion. 2,3 A study in Canada showed the incidence to occur in 2.6% of emergency department visits and 3.5% of hospital admissions. The incidence of hyperkalemia has been reported anywhere from 2.6% to 3.2% in the United States. Most individuals with hyperkalemia are usually asymptomatic or present with nonspecific signs and symptoms (e.g., weakness, fatigue, or gastrointestinal hypermotility). 1 It is a common metabolic disorder that can lead to clinical manifestations such as hemodynamic instability, neurologic sequelae, and fatal arrhythmias. Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium concentration of >5.5 mEq/L in adults. A new drug (patiromer) was recently approved for the treatment of hyperkalemia, and additional agents are also in development. Other treatment options for hyperkalemia include IV calcium, insulin, sodium bicarbonate, albuterol, and diuretics. Up until recently, FDA-approved therapies for the management of hyperkalemia (i.e., sodium polystyrene sulfonate) had remained unchanged for over 50 years. ABSTRACT: Hyperkalemia (elevated serum potassium) can become a life-threatening electrolyte abnormality due to medication use, kidney dysfunction, or alternative sources of electrolyte imbalance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
